Ginseng
 Ginseng (Panax ginseng) is a root that Native Americans, the Chinese, and Koreans have been using for centuries because of its medicinal properties. Ginseng has obvious therapeutic benefits and has traditionally been used as a preventative medicine. If taken frequently, ginseng is reputed to increase life span and improve vitality. Ginseng (Panax ginseng) is a root that Native Americans, the Chinese, and Koreans have been using for centuries because of its medicinal properties. Ginseng has obvious therapeutic benefits and has traditionally been used as a preventative medicine. If taken frequently, ginseng is reputed to increase life span and improve vitality.
Background and History of Ginseng
Ancient Chinese cultures believed ginseng helped the soul and the heart in equal measure. Its historical use can be traced as far back as 5,000 years. Native Americans have also long been using North American ginseng because of its various health benefits.
Ginseng Etymology (Name Origins)
 Panax ginseng’s name comes from its distinctive human-like shape. Most commonly referred to as ginseng, this name derives from the Chinese word "r�nsh�n" which means "man root" in English. Panax ginseng’s name comes from its distinctive human-like shape. Most commonly referred to as ginseng, this name derives from the Chinese word "r�nsh�n" which means "man root" in English.
The scientific origins comes from the word 'Panax'. The first part of this word, "Pan", means "all" in Greek; the second part, "Akos", is based on the Greek word for "remedy" or "cure".
Different Names of Ginseng (Synonyms)
Ginseng has several names, but normally they are differentiated by the region where Ginseng grows, and by its appearance:
 By the Region: By the Region:
• Korean ginseng
• Siberian ginseng
• Panax (Syn. Asian ginseng, red ginseng)
• Panax Quinquefolius (Syn. American ginseng)
By its Appearance:
• Red ginseng
• White ginseng
How Does Ginseng Grow?
 Wild ginseng grows in cooler locations, and needs to be in the shade for between 70-90% of the day, with temperatures of 50 degrees Fahrenheit. Its natural environment should be imitated as closely as possible, in order for the herb to grow domestically. Wild ginseng grows in cooler locations, and needs to be in the shade for between 70-90% of the day, with temperatures of 50 degrees Fahrenheit. Its natural environment should be imitated as closely as possible, in order for the herb to grow domestically.
These methods are adhered to on large-scale ginseng farms, which only grow this herb.
Click on the following link to read more information about ginseng, or continue reading to learn about the different types of ginseng.
Types of Ginseng
Different types of ginseng grow around the world, from the mountains of China to the Canadian state of Ontario. The main types of ginseng available are:
Panax:
 Often known as Asian ginseng (root), this is used in ancient Chinese medicine to increase Yang energy. This type of ginseng stimulates the body and has a positive effect on circulation. Asia and some parts of Russia are the main locations in which this type of ginseng grows. Often known as Asian ginseng (root), this is used in ancient Chinese medicine to increase Yang energy. This type of ginseng stimulates the body and has a positive effect on circulation. Asia and some parts of Russia are the main locations in which this type of ginseng grows.
 Panax Quinquefolius: Panax Quinquefolius:
While Asian ginseng promotes Yang energy, the American Panax root is said to increase Ying energy. Climates such as that in the American state of Wisconsin enable the growth of this particular ginseng. Panax Quinquefolius is believed to clean out any excess Yang energy, and calm the body.
Less well-known types of ginseng include:
• Red ginseng
• Wild ginseng
• Siberian ginseng
• Korean ginseng
Click on the following link to read more information the different types of ginseng, or continue reading below to find out how ginseng works with the body.
How Does Ginseng Work?
 Ancient cultures around the world have been using ginseng for centuries. One of the main reasons ginseng is so popular is because it is a phytoestrogenic herb which means it contains human-like hormones that can help women suffering from the effects of hormone imbalance. Ancient cultures around the world have been using ginseng for centuries. One of the main reasons ginseng is so popular is because it is a phytoestrogenic herb which means it contains human-like hormones that can help women suffering from the effects of hormone imbalance.
Another reason ginseng is often prescribed is due to its unique chemical properties. Ginseng is the only known herb that contains ginsenosides - a steroid-like compound that helps increase vitality, energy, and stamina.
Ginseng Properties
Because of its beneficial properties, ginseng has long been favored as a medicinal herb. It is the only herb that contains the chemical compound ginsenosides, and its health benefits are derived from this compound.
Ginsengs beneficial effects are because of Ginsenosides and this compound is similar to the steroid-like compound: triterpene saponins.
How Ginseng Works With the Body
Ginseng interacts with the body in two ways:
 The first way is on a hormonal level. Ginseng substitutes human hormones with phytoestrogenic ones, and this increases estrogen levels in the body. The first way is on a hormonal level. Ginseng substitutes human hormones with phytoestrogenic ones, and this increases estrogen levels in the body.
The second way that ginseng works with the body is via the compound ginsenosides. Ginsenosides are known to increase stamina and energy levels in humans, due to them being an adaptogen.
Click on the following link to read more about how ginseng works, or continue reading to learn about its different uses.
What is Ginseng Used For?
The type of ginseng root grown often determines the manner in which it is used. In some parts of Asia, the healing properties of ginseng are based on tradition, culture, and historical experience. In the Western world, the herb has come under scrutiny as scientists continue to work out how to use the root most effectively in modern day medicine.
Cultural Practices and Traditional Uses of Ginseng
 The Native Americans and the Chinese consumed ginseng in order to accelerate the recovery process, and strengthen resistance to illness. Throughout history ginseng has primarily been used to improve resistance and revitalize the body. The Native Americans and the Chinese consumed ginseng in order to accelerate the recovery process, and strengthen resistance to illness. Throughout history ginseng has primarily been used to improve resistance and revitalize the body.
Modern Day Uses of Ginseng
In the Western world, ginseng’s uses are the subject of extensive scientific trials. Such trials aim to test the efficiency of ginseng in treating specific modern day ailments. Some of these include:
As an Energizer: To assist the body’s natural capacity to heal. For this reason, both the American and Asian ginseng are often used in the process of rehabilitation for people recovering from injury or illness.
As Treatment for Sexual Dysfunction Problems: As a renowned stimulant, red ginseng is often used to help correct sexual dysfunction.
For Treating Menopause Symptoms: Ginseng has differing results depending on the person taking it. Despite these varying effects, many women take ginseng to lessen the often agonizing symptoms of menopause.
Ginseng is sometimes prescribed to treat mental well-being because it is considered a "normalizer" and "energizer". It is also a proven reliever of fatigue, nervousness, and stress.
Different Ginseng Products
Ginseng is sold in different forms. These include:

• Tea
• Powder
• Extract
Ginseng Overdose
Consuming vast quantities of ginseng is harmless. For people who may be more susceptible to its phytoestrogenic effects, such as those with hormone-dependant cancers, the risks involved with taking too much ginseng are greater. Common side effects of ginseng include:
• Low blood sugar.
• A rapid heart beat.
• Easy bruising.
Prolonged cases of any of the above or symptoms which worsen is one of the clearest indicators of an overdose.
Click on the following link to read more about how ginseng is used, or continue reading to learn more about the benefits of ginseng.
Ginseng Benefits
Ginseng has been used for almost 5,000 years to help the body fight illness. For this reason it’s known as the "all-healing" herb. It is used to speed up recuperation from injury or ill health as well as to revitalize the body. Ginseng’s present day usage has grown considerably, as a result of research showing its beneficial interactions with the human body.
Specific Ginseng Health Benefits
 Hormonal Problems: All forms of the ginseng Panax root contain plant hormones that are akin to human estrogen. This is because ginseng is a phytoestrogenic herb. Ginseng restores hormone imbalance by substituting human hormones with phytoestrogenic ones. Because of this, ginseng is able to help treat vaginal dryness, a common symptom of menopause. Hormonal Problems: All forms of the ginseng Panax root contain plant hormones that are akin to human estrogen. This is because ginseng is a phytoestrogenic herb. Ginseng restores hormone imbalance by substituting human hormones with phytoestrogenic ones. Because of this, ginseng is able to help treat vaginal dryness, a common symptom of menopause.
Allergies: Clinical studies have shown that ginseng can be used to treat some allergies.
Cold: The North American version of ginseng contains polysaccharides and oligosaccharides, which counteract the effects of the common cold.
Sexual Dysfunction: Loss of libido is a common menopausal symptom and ginseng has been taken for many years in parts of Asia to curb this problem.
Memory Loss: Studies have shown that combining ginseng and gingko biloba can help boost brain power.

Immunity: Both American and Asian ginseng are known to boost the immune system and help the body to fight illness.
Stamina: Ginseng is often used to increase stamina. Korean ginseng is particularly popular among athletes for improving their performance.
Click on the following link to read more about the benefits of ginseng, or continue reading to find out about its side effects.
Ginseng Side Effects
Despite its numerous health benefits, ginseng can cause various side effects. Phytoestrogenic herbs like ginseng affect estrogen levels in the body and for this reason, they can produce dangerous side effects.
Common Side Effects of Using Ginseng:
Diarrhea: The natural intestinal balance for some can sometimes be disrupted by consuming Siberian ginseng.
 Heart Palpitations: Consumption of ginseng may cause slower intensified heartbeats. This is due to ginseng being an adaptogen, a herb which relaxes the body. Heart Palpitations: Consumption of ginseng may cause slower intensified heartbeats. This is due to ginseng being an adaptogen, a herb which relaxes the body.
Insomnia: Ginseng has been reported to cause restless nights for some people due to its stimulant properties.
High Blood Pressure: An increase in blood pressure is a possible side effect for those who consume Panax ginseng.
Nervousness and Agitation: Some people may experience these two symptoms to varying degrees when they first start taking ginseng.
Headaches and Difficulty Concentrating: This side effect is due to ginseng’s stimulant effects.
Interactions between Ginseng and Health Conditions
Diabetes: Consumption of ginseng may lower blood sugar levels.
Heart Conditions: Taking ginseng can sometimes cause heartbeats to slow. In this instance, the body may increase the force of heartbeats to compensate and this can cause problems for people with heart conditions.
Cancer: Ginseng can sometimes lead to complications for those with hormone-dependant cancers. This is because ginseng introduces artificial hormones into the body.
Surgery: American ginseng has been known to lower blood glucose levels. Caution should be taken when taking ginseng as the stability of blood glucose levels is important in assisting a patient’s recovery from surgery.
Some Menopause Symptoms: Women suffering from the side effects of menopause often use ginseng to lessen the severity of some of these. Ginseng’s side effects can be quite dangerous because as a phytoestrogenic herb, it adds estrogen-like hormones to the body.
Click on the following link to read more about the side-effects of taking ginseng, or continue reading to find out more about ginseng and menopause.
Ginseng and Menopause
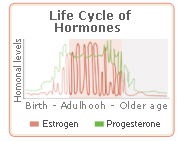 For 70% of women, menopausal symptoms begin in their early 40s. Symptoms vary from vaginal dryness to fatigue, and can often be painful and embarrassing. As a phytoestrogenic and menopause herb, ginseng can help compensate for the drop in hormone levels which cause menopausal symptoms. For 70% of women, menopausal symptoms begin in their early 40s. Symptoms vary from vaginal dryness to fatigue, and can often be painful and embarrassing. As a phytoestrogenic and menopause herb, ginseng can help compensate for the drop in hormone levels which cause menopausal symptoms.
Ongoing clinical studies show that ginseng’s healing properties come from the chemical compound ginsenosides.
Ginseng can help treat the following symptoms:
 Fatigue: Women may experience a general lack of energy, tiredness, and weakness. Ginseng is scientifically proven to curb the effects of fatigue. Fatigue: Women may experience a general lack of energy, tiredness, and weakness. Ginseng is scientifically proven to curb the effects of fatigue.
Vaginal Dryness: As a direct result of a drop in estrogen levels, this symptom occurs when the walls of a women’s vagina start to lose the soft inner lining. Ginsenosides have an estrogen-like effect on vaginal walls, which prevents the thinning of tissue and can stop vaginal dryness.
Disturbing Memory Lapses: An increase in stress levels is usually the cause of this mental state. Combining ginseng with the herb ginkgo can help combat this by stimulating mental capacity.
Increase in allergies: Ginseng can help the body fight off the spread of allergies, by boosting the immune system.
There are other, more common symptoms where ginseng isn’t capable of providing any help at all. These include:
 • Hot Flashes • Hot Flashes
• Night Sweats
• Breast Tenderness
• Irregular Periods
• Mood Swings
Click on the following link to read more information about ginseng and menopause.
Conclusions about Ginseng
Ginseng is great for treating some menopause symptoms, but has recently been criticized because it adds artificial hormones to the body. In doing so, ginseng can trigger side effects including serious conditions such as breast cancer.
Other alternative treatments are just as effective as ginseng, but without the side effects. Non-estrogenic herbs, for example, are great for treating menopause symptoms. Read more in the following article.
Which herb should women try? Today women are looking for relief from their menopause symptoms with herbs. Phytoestrogenic herbs and non-estrogenic herbs are good in relieving menopause symptoms, but recent studies show that non-estrogenic herbs have no side effects because they help the body to produce its own hormones instead of introducing hormones like the phytoestrogenic ones. Learn more about non-estrogenic herbs for menopause. | 

