What is Ginseng?
Ginseng (Panax ginseng) is a root that has been used as medicine among Native Americans, the Chinese, and Koreans for thousands of years. This herb is traditionally used as a preventative medicine, but it has exceptional therapeutic benefits too. If taken regularly, ginseng herb enhances vitality, and is reputed to lengthen life span.
Ginseng�s health benefits can be traced back to its historical and etymological roots, both of which are detailed below.
Background and History of Ginseng
 Ginseng�s history can be traced as far back as 5,000 years when the Chinese discovered its positive effects on spiritual and physical well-being. Ancient Chinese cultures believed it served the soul and the heart in equal measure. They also believed that ginseng could lengthen life span and increase stamina. Ginseng�s history can be traced as far back as 5,000 years when the Chinese discovered its positive effects on spiritual and physical well-being. Ancient Chinese cultures believed it served the soul and the heart in equal measure. They also believed that ginseng could lengthen life span and increase stamina.
Across continents, Native Americans had long been cultivating North American ginseng for its health benefits. This cultivation greatly increased with the arrival of the first European settlers, who appreciated the beneficial effects of ginseng.
The importance of ginseng in these two continents led to the first trade route of the herb being established between China and North America.
Ginseng Etymology (Name Origins)
 Ginseng comes from the Chinese word "r�nsh�n" meaning "man root." Its name is derived from its distinctive human-like appearance, complete with forked legs, resembling that of a man. Ginseng comes from the Chinese word "r�nsh�n" meaning "man root." Its name is derived from its distinctive human-like appearance, complete with forked legs, resembling that of a man.
The scientific etymology of the name stems from the word Panax. The first part of this, �Pan�means "all" in Greek; the second part, "Akos" is based on the Greek word for "cure" or "remedy". Such a name is steeped in the curative properties that have made ginseng one of the world's most sought-after herbs.
Panax ginseng is just one type of ginseng. This herb has a variety of names and synonyms, which are explained in more detail below.
Different Names of Ginseng (Synonyms)
Ginseng has several names that vary due to the region they grow in, and their appearance. Below is a list of these names and their respective synonyms:
 By the Region: By the Region:
. Korean ginseng
. Siberian ginseng
. Panax (Syn. Asian ginseng, red ginseng)
. Panax quinqufolius (Syn. American ginseng)
. (Wild ginseng is a name given to a version of this herb that grows in the wild and can be applied to any ginseng of the above regions).
By its Appearance:
. Red ginseng
. White ginseng
Despite their differing names and appearances, all types of ginseng grow in the same way. The conditions for this growth are looked in the next section.
How Does Ginseng Grow?
 Wild ginseng grows in temperate climates and flourishes in temperatures of 50 degrees Fahrenheit, with 70-90% shade. To cultivate the root, the conditions of its natural environment should be copied as closely as possible. Wild ginseng grows in temperate climates and flourishes in temperatures of 50 degrees Fahrenheit, with 70-90% shade. To cultivate the root, the conditions of its natural environment should be copied as closely as possible.
 The soil required for domestic cultivation of ginseng should be well-drained and the seeds should be placed at least 12 inches into the soil. The soil required for domestic cultivation of ginseng should be well-drained and the seeds should be placed at least 12 inches into the soil.
Such cultivation methods are used on large-scale ginseng farms, which exclusively grow this herb.
The product of such cultivation is a distinctly unique looking plant and root. Continue reading to find out what ginseng looks like.
What does Ginseng Look Like?
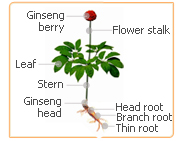 Based on ginseng�s etymology, this "man root" has a human-like shape. A fully mature root usually forks into what resembles the legs of a man, with the top of the plant forming the head. In China, roots that closely resemble this shape are considered most beneficial to a person's health. Based on ginseng�s etymology, this "man root" has a human-like shape. A fully mature root usually forks into what resembles the legs of a man, with the top of the plant forming the head. In China, roots that closely resemble this shape are considered most beneficial to a person's health.
 This green-leafed perennial plant changes in appearance during every year of its life. It is easily identifiable in its third year, when it sprouts yellow-green flowers. The most easily recognizable type of ginseng is red ginseng; it looks vibrantly different to the matured form of white ginseng due to it being either marinated or sun dried. This green-leafed perennial plant changes in appearance during every year of its life. It is easily identifiable in its third year, when it sprouts yellow-green flowers. The most easily recognizable type of ginseng is red ginseng; it looks vibrantly different to the matured form of white ginseng due to it being either marinated or sun dried.
In contrast to the other types of ginseng, Siberian ginseng was named for branding purposes only, and it looks different too, resembling a thin tree bark.
Now that what ginseng is and its origins have been explained. Keep reading to find out more about the different types of ginseng.
Conclusions about Ginseng
Ginseng is great for treating some menopause symptoms, but it has recently been criticized because it adds artificial hormones to the body. In doing so, ginseng can trigger side effects, including serious conditions such as breast cancer.
Other alternative treatments are just as effective as ginseng, but without these side effects. Non-estrogenic herbs, for example, are great for treating menopause symptoms. Read more in the following article.
Which herb should women try? Today women are looking for relief from their menopause symptoms with herbs. Phytoestrogenic herbs and non-estrogenic herbs are good in relieving menopause symptoms, but recent studies show that non-estrogenic herbs have no side effects because they help the body to produce its own hormones instead of introducing hormones like the phytoestrogenic ones. Learn more about non-estrogenic herbs for menopause.
| 

